Rwanda Continues to Shine in Export Growth as Locally-Made Products Rise by Over 11%
Rwanda’s commitment to strengthening its export-driven economy is bearing fruit, with new statistics showing a significant growth in locally-produced goods reaching international markets.
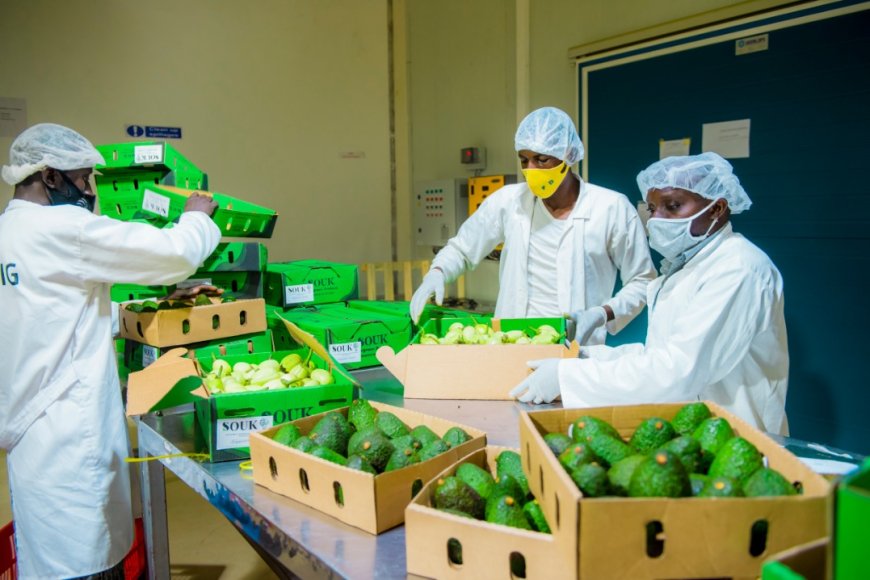
A report released on July 21, 2025, by the National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR), reveals that domestic exports rose by 11.40% in the first quarter of 2025 compared to the same period last year. Goods made in Rwanda generated RWF 688 billion (approximately $480.82 million), up from RWF 617 billion ($431.61 million) in Q1 2024.
This rise is seen as a key indicator of Rwanda’s resilience and long-term commitment to expanding its industrial base and diversifying its exports.
“This steady increase confirms Rwanda’s capacity to produce competitive goods for international markets and highlights the growing role of local industries in economic transformation,” the report noted.
Despite this growth in domestic exports, the report also points to a decline in imports and re-exports, suggesting shifts in trade dynamics. Rwanda’s imports in Q1 2025 stood at RWF 1,975 billion ($1.38 billion), a 2.23% decrease from the same period last year. Similarly, re-exports dropped by 21.82%, totaling RWF 194 billion ($135.39 million).
Overall, the country’s total trade volume in Q1 2025 reached RWF 2,859 billion ($1.99 billion), a marginal decline of 0.99% compared to Q1 2024.
Key destinations for Rwanda’s domestic exports included the United Arab Emirates, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), China, Luxembourg, and the United States of America. Among the top re-exported items were food products and live animals, valued at RWF 61 billion ($42.33 million), and petroleum products, worth RWF 49 billion ($34.35 million).
On the import side, China, Tanzania, Kenya, India, and the United Arab Emirates remained Rwanda’s top trading partners.
The report underscores that while there was a drop in overall trade value, the continued rise in homegrown exports serves as a cornerstone for sustainable economic development. Experts view this trend as an encouraging sign that Rwanda’s Made-in-Rwanda policy and broader industrialization efforts are gaining traction.
As the country seeks deeper integration into African and global markets through regional blocs such as the East African Community (EAC), COMESA, and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), this momentum in domestic production is expected to bolster Rwanda’s ambition to become a regional trade and manufacturing hub.


 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
 English
English
 Swahili
Swahili