NISR Survey Highlights Health Improvements, with 6% Decline in Child Stunting
The National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR) has unveiled the findings of the 7th Demographic and Health Survey (DHS7), revealing notable improvements in key health indicators across the country, particularly in child nutrition and maternal health.
The survey was officially presented at the Kigali Convention Centre in the presence of senior government officials, representatives from local and international organizations, development partners, and other stakeholders.
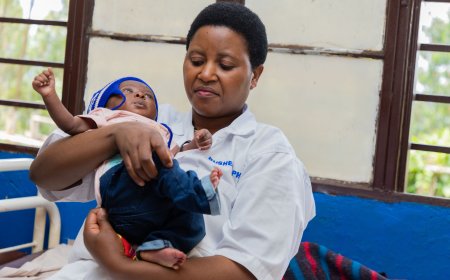
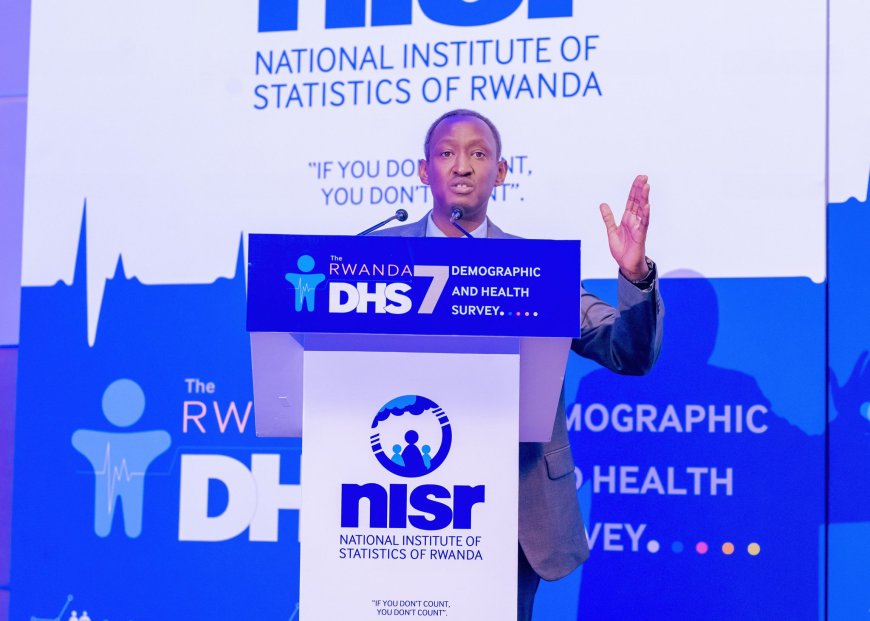
According to NISR Director General Ivan Murenzi, child stunting among children under the age of five declined to 27 percent in 2025, down from 33 percent recorded in the 2019/2020 survey, representing a six-percentage-point reduction. He described the progress as an important milestone in Rwanda’s efforts to improve child nutrition and overall well-being.
The survey also shows a steady decline in fertility rates. The total fertility rate among Rwandan women dropped from 4.1 in 2019/2020 to 3.7 in 2025, reflecting increased access to and use of family planning services.
Significant gains were recorded in maternal and child health services. Institutional deliveries have reached 98 percent nationwide, contributing to a reduction in neonatal mortality from 45 to 36 deaths per 1,000 live births. Maternal mortality also declined substantially, falling from 203 to 149 deaths per 100,000 live births over the same period.
Despite these positive trends, the DHS7 highlights emerging and persistent challenges. Teenage pregnancy rates increased to 8 percent in 2025 from 5 percent in 2019/2020 among adolescents aged 15 to 19, raising concerns about adolescent reproductive health and protection.
Minister of Finance and Economic Planning Yusuf Murangwa noted that the survey provides strong evidence of Rwanda’s socio-economic progress and supports effective planning under the National Strategy for Transformation (NST2). He urged stakeholders to use the data to better target interventions and resources.
United Nations Resident Coordinator in Rwanda Ozonnia Ojielo praised the findings as a reflection of Rwanda’s commitment to improving population health, emphasizing that a healthy population is a key driver of productivity and economic growth.
Minister of Health Dr. Sabin Nsanzimana welcomed the improvements but called for intensified efforts in priority areas, particularly in reducing teenage pregnancies, accelerating the decline in newborn deaths, and further lowering child stunting rates. He stressed that while progress has been made, sustained and coordinated action is needed to achieve faster and more equitable health outcomes.
Overall, the 7th Demographic and Health Survey demonstrates Rwanda’s continued progress in improving health indicators, while providing a critical evidence base to guide future policies and investments in the health sector.







 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
 English
English
 Swahili
Swahili